Colour temperature

Generally, colour temperature is a quality feature of light, indicating whether the light colour is cold or warm. It specifies the intrinsic colour of the light emitted by a lamp. Red and blue are of major importance here. The higher the red component in the light, the warmer the light; the higher the blue component in the light, the colder it is.
The colour temperature of different light sources:
Candle
1,800 K = extremely high red component = flattering, dim light
Incandescent lamp
2,700 K = very high red component = warm, cosy light
Halogen lamp
3,000 K = high red component = warm, cosy light
Fluorescent lamp 840
4,000 K = balanced blue and red component = neutral, clear light
Daylight
6,000 - 20,000 K = high blue component = fresh, natural, energising light
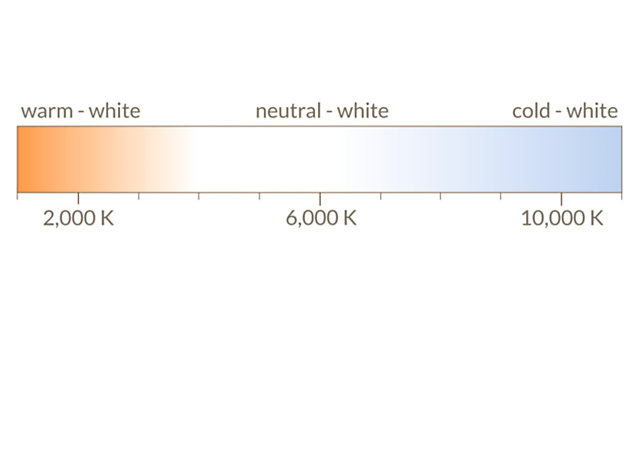
Determining the colour temperature
The colour temperature is measured in degrees Kelvin (K). There are usually three categories for the colour temperature. In the case of a temperature below 3,300 Kelvin, the light is described as warm-white; a colour temperature between 3,300 and 5,300 Kelvin is referred to as neutral-white and any colour above 5,300 is known as cold-white or daylight-white.
The colour temperature of a particular lamp can be found on the packaging (colour code). For instance, the energy-saving lamp TCA-SE, 20W/827, E27 has a colour temperature of 2,700 K, i.e. it has a warm white light colour. This can be seen from the last two numbers of the code 827.

